A consultation with Dr. Sophie Armstrong involves the following:
- Diagnosis of injury
- A thorough clinical examination
- Treatment of injury symptoms
- Investigation recommendations
- Management strategies related to the injury or ailment
- Patient education to help avoid future injury occurrence
- Assessment and treatment of chronic medical conditions
- A personalised exercise and recovery program
- Access to allied professional health services such as physiotherapy, podiatry and nutrition
- Communication with your GP and existing or referring health and exercise professionals.
Patients can expect a sound overview and understanding of their condition with an appropriate strategy moving forward.
Interventions

A corticosteroid injection works to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. The effects of the injection usually last from several weeks to three months, providing an optimal time for healing and to perform any required rehabilitation. Corticosteroid injections have a role in treating inflammatory problems such as bursitis, impingement, tendinopathy, osteoarthritis and inflammatory joint disease.
- The risks of a corticosteroid injection are very low and will be discussed with you before your injection.
The procedure is relatively non-invasive and may be performed with ultrasound guidance. The injection area can often be irritable for a day or two. Usually you are able to walk or drive afterwards without issue. You will normally be asked to rest the affected area for several days afterwards. Some areas may need more strict rest for a longer period depending on the condition being treated.
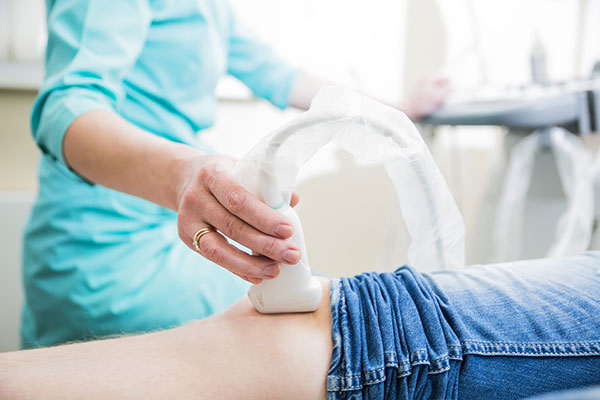
Ultrasound provides a view of internal body structures enabling accurate location of potentially injured joints and tendons.
Ultrasound guided injections are commonly used for treating sports injuries. The needle is guided under direct visualisation with the ultrasound to the targeted structure. The ultrasound provides anatomic information and a view of the injected material as it enters the target area. This allows accurate placement of the injection into a joint, bursa, tendon or tendon sheath.
The areas most commonly targeted are the shoulder, elbow, hip or foot or ankle. For some injections use of the ultrasound is not required, many knee or ankle joint injections can be successfully performed using appropriate non-guided techniques.
The Procedure
The injection(s) occur in the normal clinic consulting room. You will be positioned comfortably, the area to be injected will be marked and the skin cleaned. The ultrasound machine is used to watch the tip of the needle as it is injected into the affected area. The technique can vary depending on the joint or structure targeted.
Ultrasound guided injections take approximately ten minutes to administer with little to no downtime required after the procedure.

Viscosupplementation (Hyaluronic acid) injections can provide relief from joint pain related to osteoarthritis with the aim to improve function.
What is Hyaluronic Acid?
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring component of cartilage and synovial fluid. It facilitates the sliding properties enabling pain free movement of knees and other joints; it calms inflammation and encourages associated anti-inflammatory molecules to become more active in the treated area.
The Hyaluronic Injection
Hyaluronic acid injections assist by supplementing depleted viscous materials of the joint in a process called viscosupplementation. The knee is the most typically treated joint. Over time the injected hyaluronic acid is absorbed into the surface of the joint where it has the potential to modify inflammation within the joint, which helps reduce pain and improve strength and function.
When to Consider Viscosupplementation
Viscosupplementation can be recommended as an additional treatment or stand-alone procedure depending on individual considerations related to osteoarthritis. Especially if other treatment measures for example painkillers, anti-inflammatory tablets or steroid injections are ineffective.
Hyaluronic acid is generally well tolerated, with minimal potential side effects, and may help to avoid longer-term use of pain relieving medications.
PRP is designed to accelerate healing of tendon injuries and osteoarthritis naturally. PRP technology was initially developed over 20 years ago to abide wound healing and blood loss. But now its benefits are being used towards facilitating tendon and pain management.
Patients should consider PRP treatment if they have been diagnosed with any of the following:
- Various tendinopathies e.g. elbow, knee, gluteal, hamstring, Achilles
- Rotator cuff tears of the shoulder
- Plantar fasciosis
- Osteoarthritis
The Procedure
The patient’s own blood is used. Specially prepared platelets are taken and then re-injected into the affected area. These platelets release substances known as growth factors that can promote tissue healing.
Depending on a patient’s condition, a series of 1 to 3 injections may be required at 4 to 6 week intervals.
Initially, the procedure may cause some localised pain and discomfort. Patients can apply ice and elevate as needed. After one-week rehabilitation program can be commenced or re-commenced.
Although uncommon, the risks include signs and symptoms associated with an injection. These include pain, infection, no relief of symptoms, worsening of symptoms, blood clot, nerve injury, skin discolouration, calcification, scarring, loss of fat to the affected area, and allergic reaction. If any of these are experienced, please contact the clinic.
What is Radial Shock Wave Therapy (RSWT)?
RSWT is the application of a high-energy acoustic pulse transmitted into the tissue of the affected area of the body. Each RSWT treatment works to increase the metabolic activity around the site of pain or discomfort. This stimulates the body’s natural healing process, thus reducing pain and promoting the reabsorption of irritative calcium deposits in tendons.
In pain management, RSWT is usually applied in three treatment sessions, each one week apart. Approximately 80% of all patients report a substantial improvement after the second treatment.
How does it work?
C nerve fibres are responsible for transmitting pain in the body. They release a specific substance known as substance P. This substance is responsible for causing slight discomfort during and after shock wave treatment. However, with prolonged activation, C nerve fibres become incapable, for some time, of releasing substance P and causing pain.
Less substance P in the tissue leads to reduced pain and a reduction on neurogenic inflammation. A decline in neurogenic inflammation may in turn promote healing through the release of growth factors and the activation of stem cells in the treated tissue.
In the treatment of tendinopathy it is thought that the energy delivered via RSWT results in an increase in the diffusion of substances called cytokines across vessel walls into the pain-generating region. This results in the resolution of the tendinopathy via the stimulation of angiogenesis (development of new bloods vessels) and the healing process.